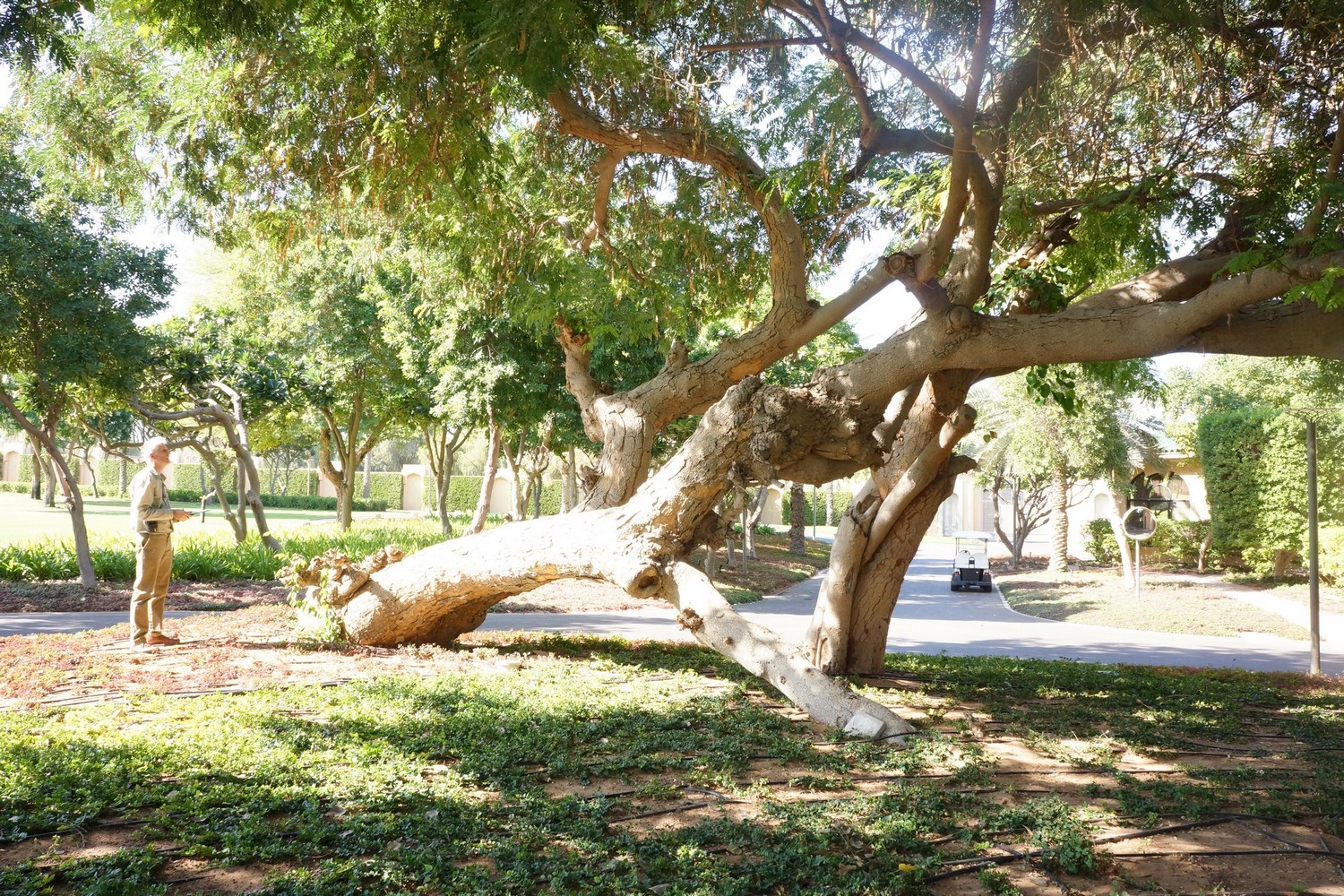
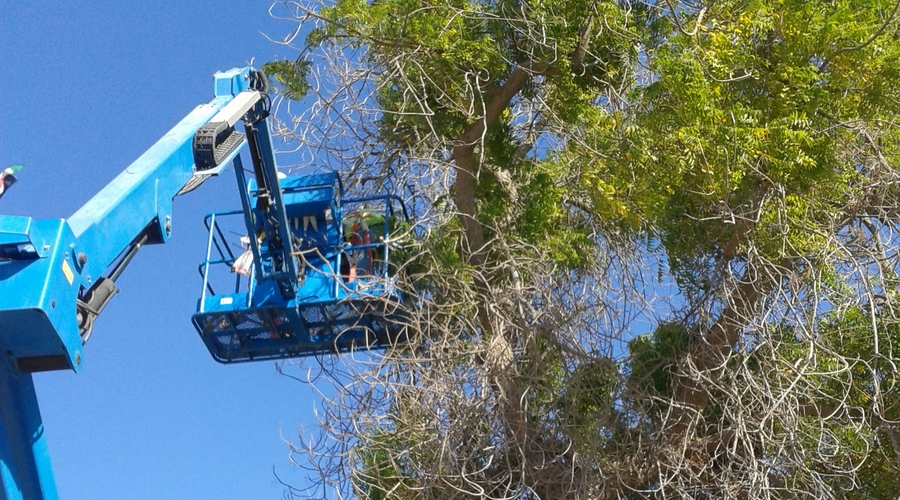
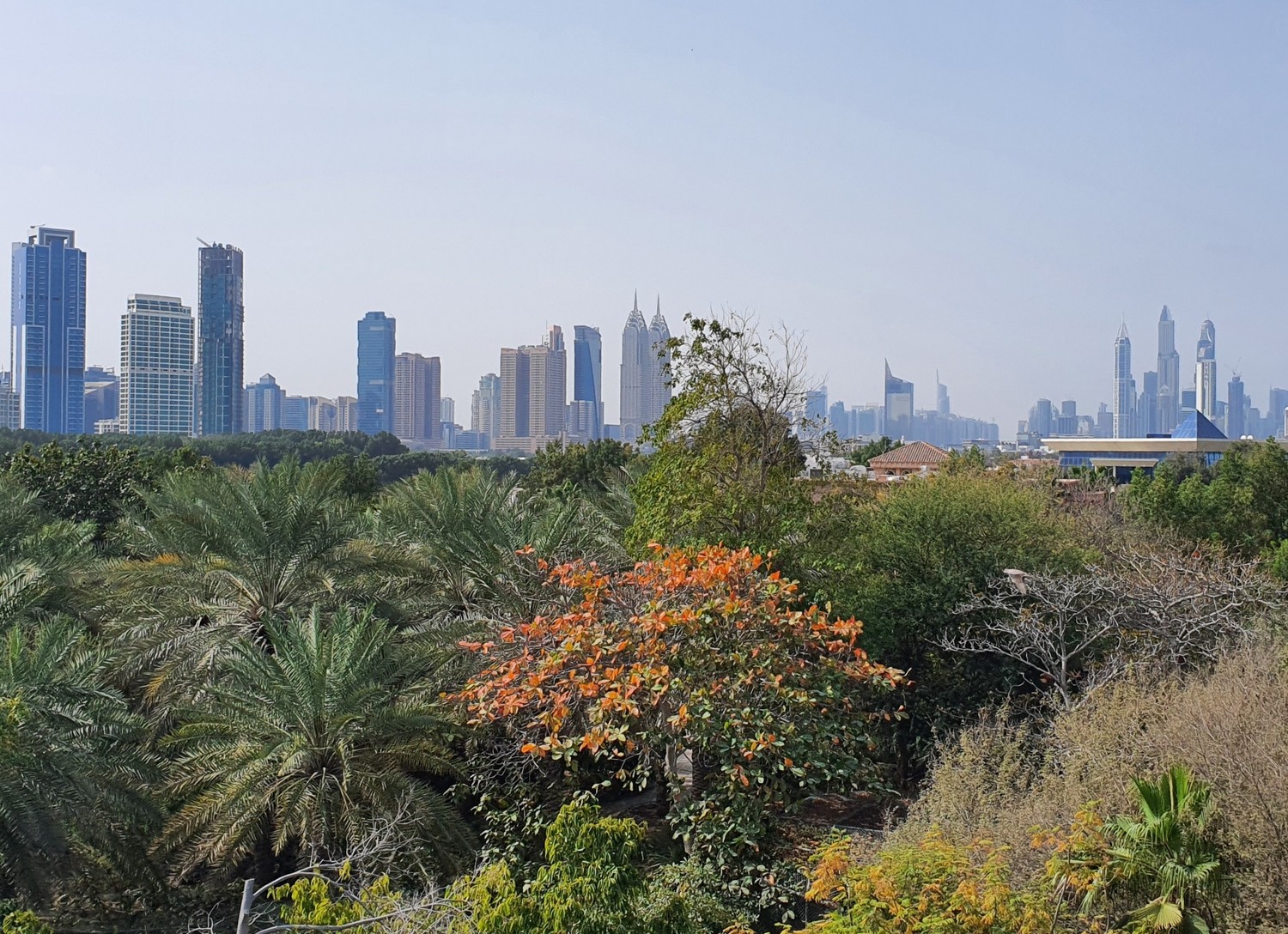
First published in Landscape Middle East magazine, September 2024 (with different title). If there is one […]
I have had another article published in Landscape Middle East magazine, as part of an on-going […]
I am currently involved in on-going consultancies giving advice on alternative tree planting methods, internal/external podium […]
I’ve been using Instagram on my main account (Mark Laurence Design) but now have one dedicated […]
On this last day of the year, it’s wet and dull outside here in the UK, […]
Due to the on-going Covid 19 pandemic I will not be travelling to the UAE (or […]
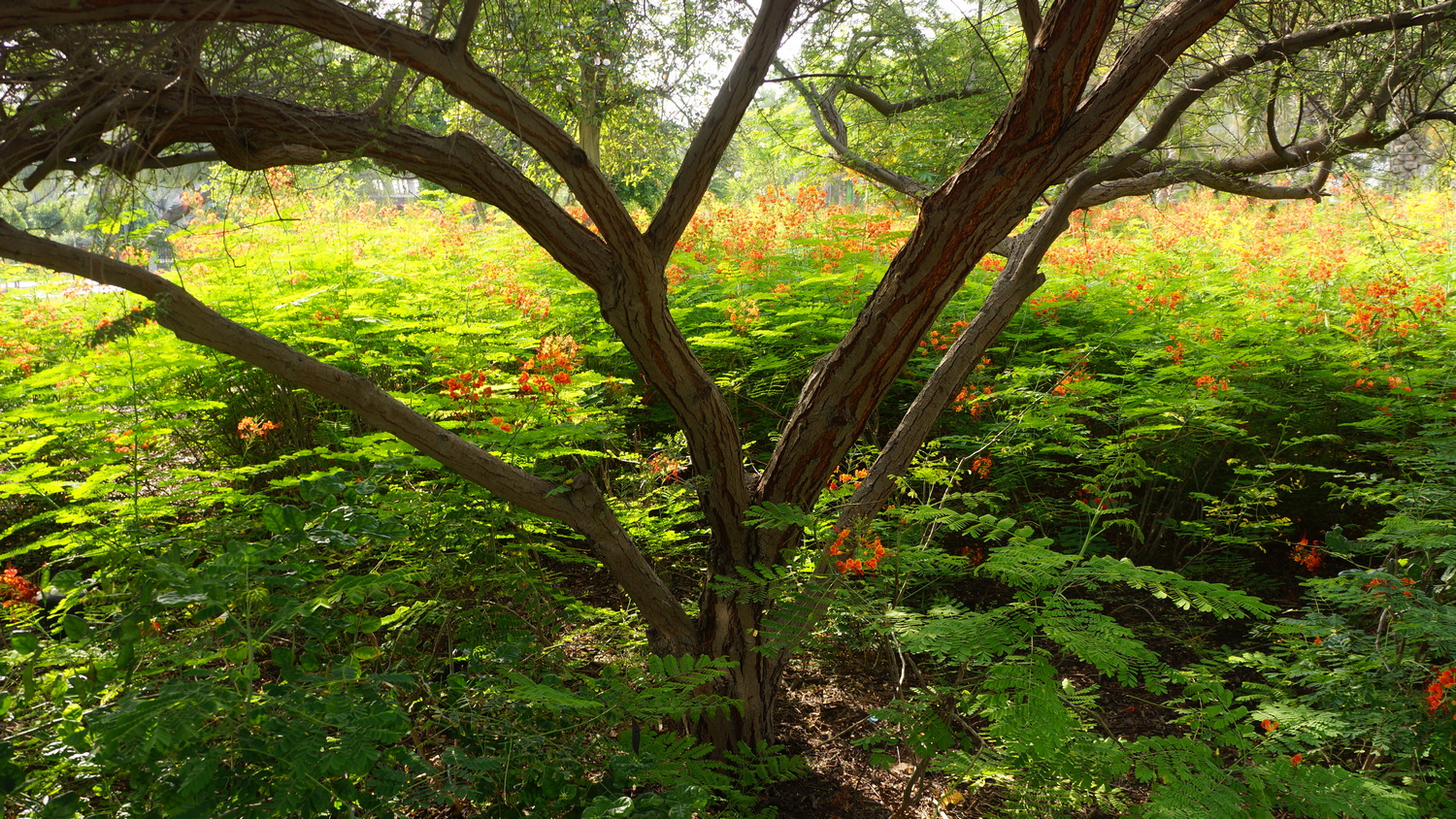
Landscapes are all about creating micro-climate, or would be, if designed for that goal. Why is […]
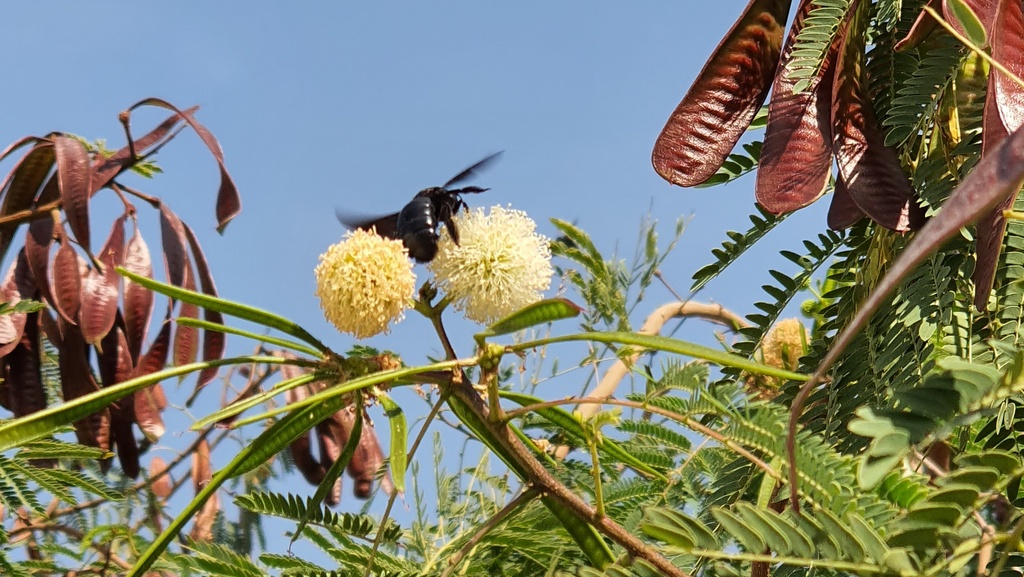
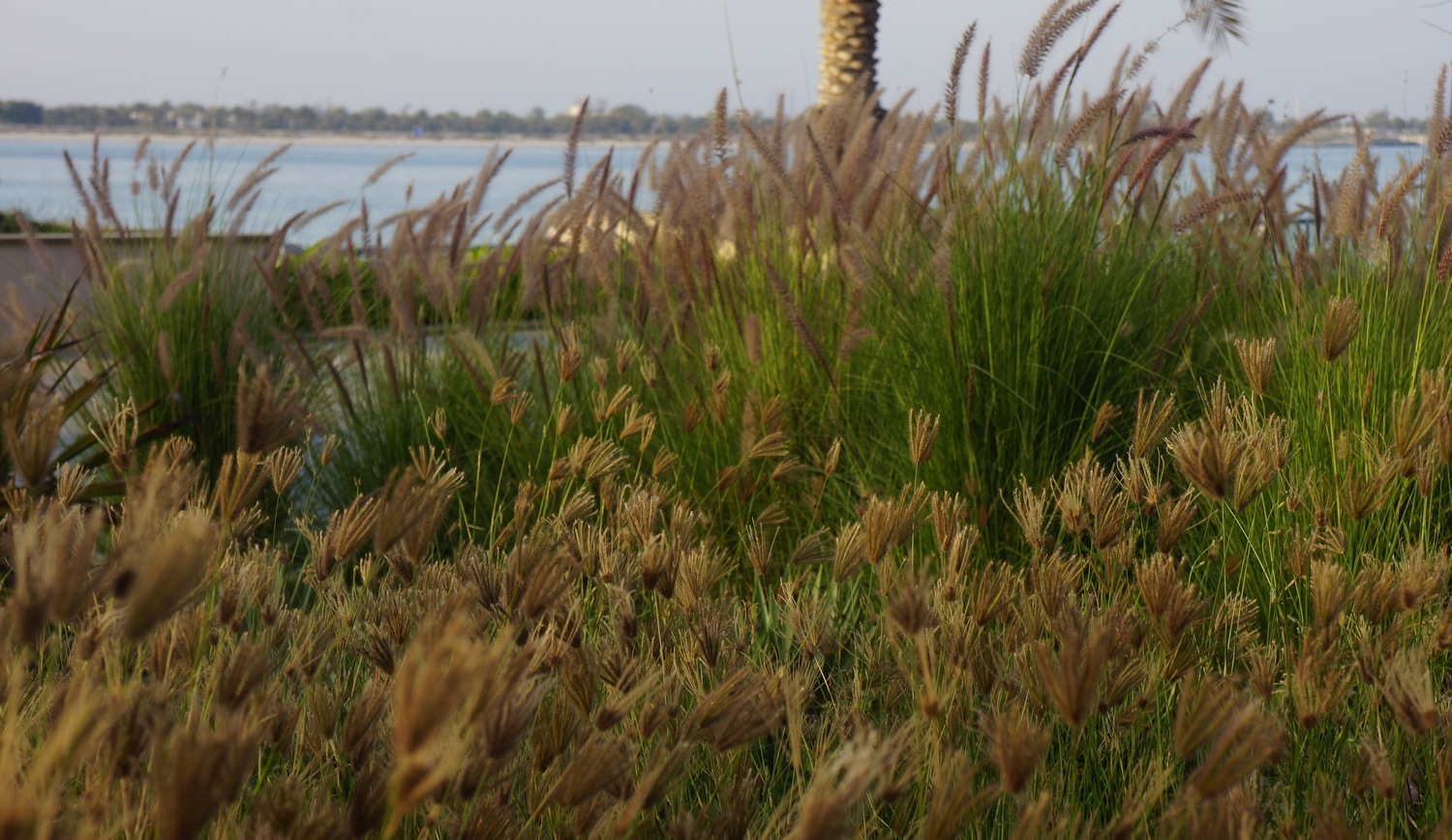
The other side of work I undertake in the Middle-East region is planting design, for creating […]